How to Solve Kites in Geometry
Multiply the lengths of two unequal sides by the sine of the angle between them. Using the Pythagorean Theorem.

Question Video Finding The Side Length Of A Kite Given Its Diagonal Lengths Nagwa
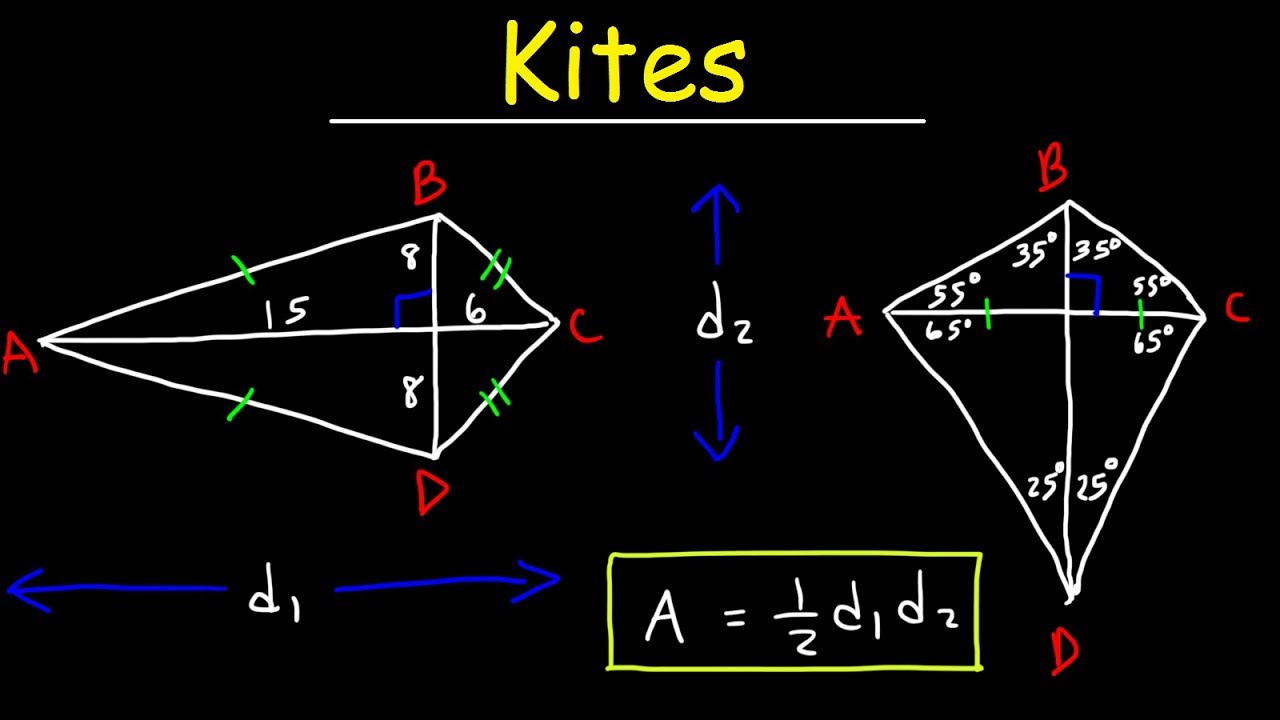
To find the area of a kite multiply the lengths of the two diagonals and divide by 2 same as multiplying by 12.

. Therefore use the Pythagorean theorem. Click on each like term. That will be the middle of KT K T.
Kite is a symmetric shape and its diagonals are perpendicular. For example if the length of the diagonals of a kite are given as 7 units and 4 units respectively we can find its area. Knowing the properties of a kite will help when solving problems with missing sides and angles.
Area of Triangle. The diagonals are perpendicular. There are two basic kite area formulas which can be used depending on which information you have.
So you measure unequal side lengths of 50 m and 65 m with an angle between them of 60. Diagonals of a kite cut one another at right angles as shown by diagonal PR bisecting diagonal QS. Disjoint means that the two pairs are totally separate.
The other thing we know about kites is that one of these lines is bisecting the other of the two. 55 Properties of Quadrilaterals Lesson A lesson on the properties of quadrilaterals parallelogram rectangle square rhombus kite trapezoid Geometry Lesson 102 area of trapezoid kite and rhombus video explaining the area of the trapezoid rhombus and kite with. From the definition a kite could be concave.
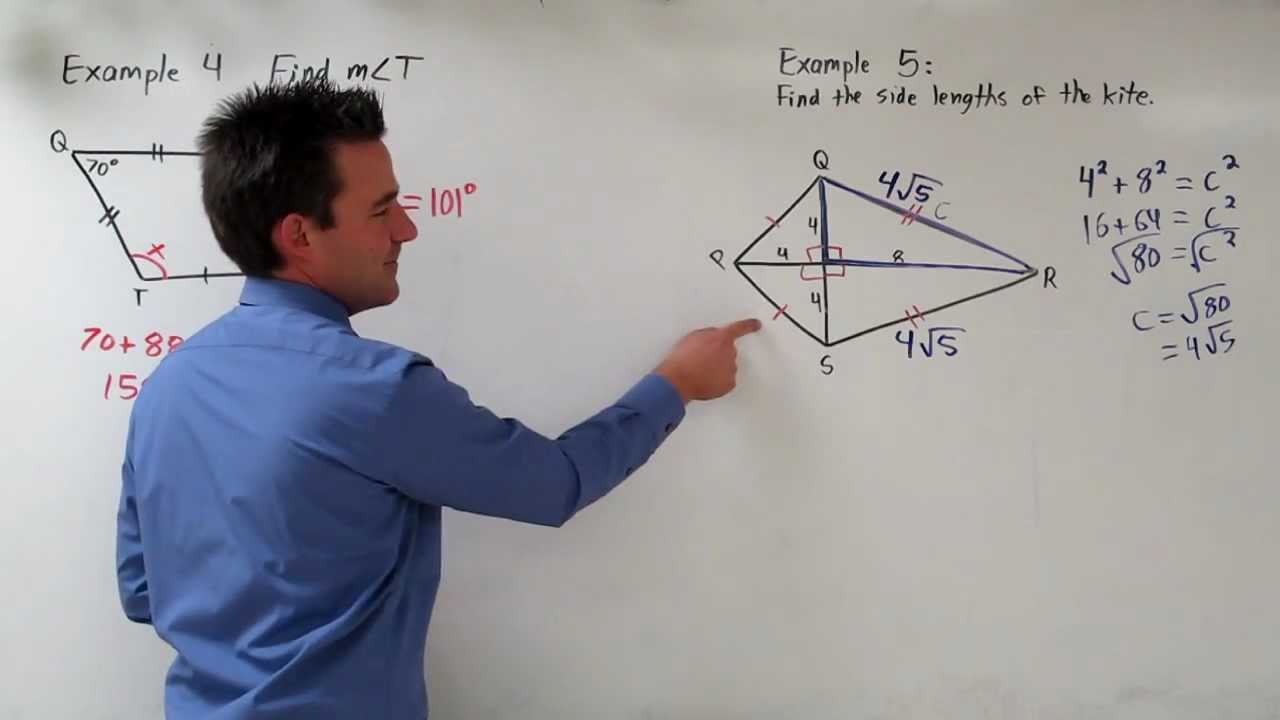
Add all known angles and subtract from 360 to find the vertex angle and subtract the sum of the vertex angles from 360 and divide by 2 to find the non-vertex angle. The sides and angles of a kite. Recall that the Pythagorean Theorem is begin aligna2b2c2end align where begin aligncend align is the hypotenuse.
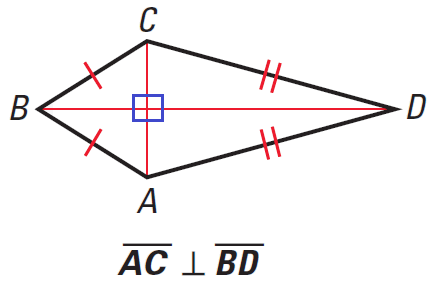
A kite is a quadrilateral with two pairs of adjacent congruent sides. One diagonal segment KM the main diagonal is the perpendicular bisector of the other diagonal segment JL the cross. Draw a dashed line to connect endpoints K K and T T.
The diagonal between the vertex angles the angles formed by two congruent sides also bisect these angles of the kite. As a result it is possible to find the measure of corresponding angles in the kite since the diagonals. The diagonals of a kite intersect at 90.
Given rectangle and equal segments. OQ OS. It looks like a kite that flies in the air.
The properties of the kite are as follows. If you know two diagonals you can calculate the area of a kite as. Mark the spot on diagonal KT K T where the perpendicular touches.
Apply the properties of the kite to find the vertex and non-vertex angles. In order to solve this problem first observe that the red diagonal line divides the kite into two triangles that each have side lengths of and Notice the hypotenuse of the interior triangle is the red diagonal. We saw that.
Kite Properties - Concept. Use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the length of the sides of the kite. This is a demo.
Learn to identify kites and trapezoids. Kite properties include 1 two pairs of consecutive congruent sides 2 congruent non-vertex angles and 3 perpendicular diagonals. It looks like the kites you see flying up in the sky.
Area e f 2 where e and f are kite diagonals If you know two non-congruent side lengths and the size of. Two disjoint pairs of consecutive sides are congruent by definition Note. After substituting the values in the formula we get Area of kite 12 7 4 14 unit 2.
Line it up along diagonal KT K T so the 90 90 mark is at I I. You could start with a line and then you could construct a perpendicular bisector of that line another. This geometry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into kites.
Additionally they contains two pairs of adjacent congruent sides. In this kite the sides are all hypotenuses. You dont want to get wet measuring the diagonals of a kite-shaped swimming pool.
Plugging the values in the formula yields eqP 2 cdot 2 sqrt 2 2 cdot 3 sqrt 2 10 sqrt 2 eq cm. Here base a and height. Kites and Trapezoids Powered by.
Area of the kite Area of triangle PQR Area of triangle PSR. There are two sets of adjacent sides next to each other that are the same length congruent. So you could actually construct a kite that way.
This is the diagonal that eventually will probably be inside the kite. It explains how to calculate the area of a kite using the length of its two diagonals. Play full game here.
O S 2 b 2. 1 2 b a s e h e i g h t. If a kite is concave it is called a dart.
Use the following properties of the kite to answer the question as asked in the problem. Check out the kite in the below figure. The formula for the area of a kite is Area 1 2 diagonal 1 diagonal 2.
To find the perimeter of a kite just add up all the lengths of the sides. Now use your protractor. Where the length of the red diagonal.
Given diagonal and angle bisector. Up to 10 cash back Explanation. One important property of kites to remember is that the diagonals of a kite form four right angles.
A kite is a quadrilateral with two distinct sets of adjacent congruent sides. 1 If the problem is asking for congruent angles identify the pair of non-vertex angles. In this lesson we learned about kites in geometry.
It can be calculated using the formula Area of kite 12 diagonal 1 diagonal 2. The area of a kite. The word distinct in the definition means that.
Comments
Post a Comment